Ransomware Update
Just as most organizations and industrial sectors had to adapt and innovate during the pandemic, cybercrime also continued to innovate...
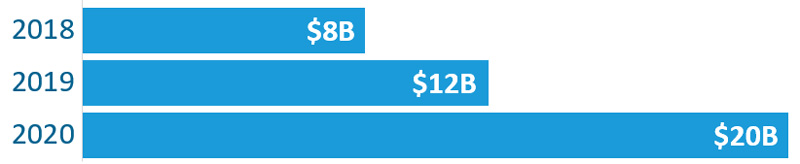
Everyone agrees that 2020 was a challenging year. It is also considered the worst year ever for ransomware. The US public sector was hit hardest, with 2,354 government, healthcare, and educational institutions compared to 1,300 private organizations, costing an estimated $20 Billion in payouts. That’s more than double the figure from 2018:
Experts believe that 2021 could be even worse.
Ransomware Advances in 2020
Just as most organizations and industrial sectors had to adapt and innovate during last year’s pandemic, cybercrime also continued to innovate in four key ways:
Marketing improvements to reach their target market. Getting around basic IT defenses such as anti-virus and anti-malware software is the first challenge for cybercriminals. Among the new 2020 tactics included:
- “Thread hacking”: the practice of spoofing a compromised email client’s account and replying to their legitimate emails, possibly including previously benign attachments along with a new malspam document that would infect the victim. (More: Emotet thread hacking)
- “Loaders”: the use of malware loading software through legitimate cloud storage such as Google Docs. In other words, instead of developing dedicated “command and control” (C&C) hacker websites, which are typically blocked by IT security products like Cisco Umbrella, cybercriminals “bypass the filter” by loading their malware onto various legitimate sites infected with “botnets” that regularly report back to C&C sites. (More: Buer Loader and BazarLoader)
Increasing sales by targeting larger organizations with the promise of even larger payouts. Several cybercrime crews have stolen a page from account-based marketing (ABM) and discovered that they can hit larger organizations effectively without increasing their overhead costs. This has trended payouts toward the high end.
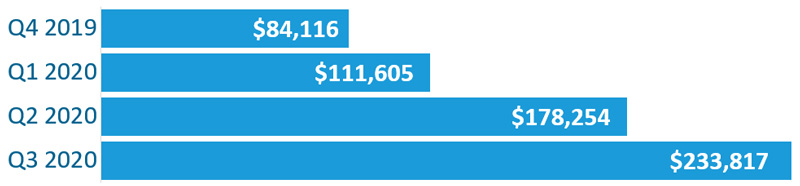
Small businesses continue to be hit as well, but their ransoms have remained relatively flat.
 “Upselling” their extortion threats through data exfiltration. Before the criminals encrypt the victim’s data, first they copy it to exfiltration servers in the cloud. While this seems like an extra and unnecessary step in the process, it provides the criminal two additional benefits:
“Upselling” their extortion threats through data exfiltration. Before the criminals encrypt the victim’s data, first they copy it to exfiltration servers in the cloud. While this seems like an extra and unnecessary step in the process, it provides the criminal two additional benefits:
- Provides insurance against IT preparedness. The victim may refuse to pay the ransom because he followed AllConnected’s backup and disaster recovery strategy, air-gapped their data with tested RPO and RTO calculations, and performed a failover and failback process so that their immediate business is not impacted by the ransomware.
However, the threat of publishing exfiltrated data across the Internet — exposing the organization to embarrassment, loss of proprietary information and clients, and potential lawsuits — encourages the victim to pay.In 2020, only the Maze crew exfiltrated data, but now there are 17 crews threatening to publish exfiltrated data if they don’t receive payments. - Establishes a side-hustle of selling exfiltrated data to other cybercrime crews. The practice is becoming so common that anyone can buy select exfiltrated data directly from the REvil crew’s website. (More: Exfiltration crews)
Industry Networking and Collaboration. Cybercrime crews are collaborating to bring to market new and more effective ransomware attacks. Following on the exfiltration tactic above, cybercriminals share stolen data and coding to create different strains of ransomware for the new year.
Remote Workers are Most Vulnerable
The pandemic forced most organizations in 2020 into work-from-home employers. Because of the speed of that transition, remote employees became low-hanging-fruit, high-value targets.
It also means that business-related cyber-attacks could now come disguised as a free trial of your child’s favorite game, or as a link to a COVID-information-related website. All that matters to the hacker is infecting that PC, now used for both work and home life, to gain access to the organization’s network once it connects.
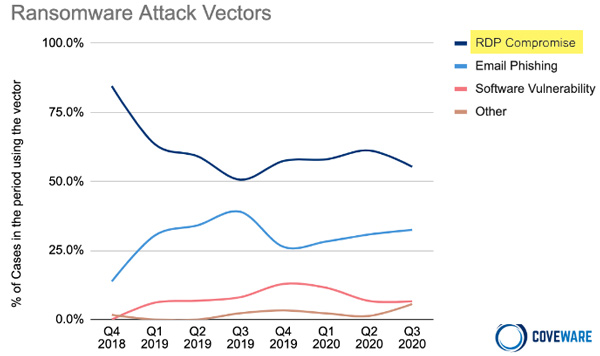
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a standard remote connection service for all current versions of Windows, used by many businesses for connecting employees suddenly forced to work from home. Unfortunately, RDP is also the number one means of breaching organizations (see chart on right).
Cloud computing, multi-factor authentication, and network perimeter security have all lessened the risk of data breaches, but they are not enough.
We recommend an IT security strategy tailored for your organization, in compliance with the latest NIST 800-171 mandate. Whether your organization works with the government, directly or indirectly, the NIST framework can help you improve the 5 core functions of cybersecurity: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover.
Tips for Preventing Ransomware
Your IT security should Whether you have an inhouse IT team or outsource significant proactive and reactive security functions to an MSP like AllConnected, the following should be implemented at your organization to reduce the risk of ransomware:
- Implement cybersecurity user awareness training for all employees. Conduct phishing tests to gauge their awareness and reinforce the importance of identifying potentially malicious email.
- Adopt a “Zero-trust” policy in regards to all email and web-browsing
- Keep Windows OS and related software up-to-date with the latest patches
- Remove unnecessary accounts, profiles and groups from systems
- Disable or delete unused legacy software
- Restrict user permissions to proprietary applications
- Use Multi-factor Authentication to reduce the possibility of credential hacking over public or unsecured wifi connections. AllConnected recommends Cisco Duo for MFA.
- Secure domain controllers (DCs). Since RDP attacks are the most common, make sure your DC controller is up-to-date and patched. Restrict access to admins only, and don’t install other software or agents on DCs.
- Use a DNS Gateway filter like Cisco Umbrella to prevent email and Internet Browsing to known C&C sites and block exfiltration of data
- Implement advanced email gateway filters to block malicious emails and Internet Protocol (IP) addresses at the firewall. AllConnected recommends Barracuda Essential Suite
- To reduce the risk of “thread hacking,” implement DMARC policy and verification. Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance (DMARC) allows senders and receivers to improve and monitor protection of the domain from fraudulent email.
- Consider disabling macros for Microsoft Excel and Word email attachments as macros can be used to deliver ransomware
- Consider implementing an intrusion detection system (IDS) to detect command and control activity and other potentially malicious network activity that occurs prior to ransomware deployment.
AllConnected recommends implementing a Managed Detection and Response service to monitor your network for out-of-the-ordinary processes, which may be precursor to a ransomware attack.
If you would like to speak with AllConnected about your options for hardening your IT security environment and mitigating your ransomware risk, please make an appointment today.